Hijama Cupping Therapy: Top 10 Benefits, Types & Important Notes
Hijama cupping is an age-old traditional therapy gaining recognition worldwide for its potential health benefits and holistic approach. As a prominent practice in many cultures, especially within Islamic medicine, hijama cupping involves creating suction on the skin to facilitate healing and detoxification. This comprehensive guide aims to elucidate everything you need to know about hijama cupping, including what it is, how it differs from other forms of cupping, its top benefits, various types, who can safely try it, and crucial safety notes.
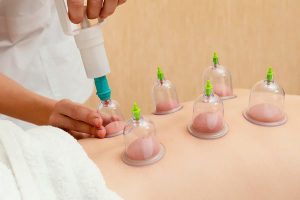
Hijama Cupping
Cupping therapy has been practiced for thousands of years across diverse civilizations, including ancient Egypt, China, Greece, and the Middle East. Today, hijama cupping refers specifically to a traditional method often performed by specialized practitioners called ‘hajams.’ The process involves placing cups—often made of glass, bamboo, or silicone—on specific points on the body, then creating a vacuum that pulls the skin upward into the cup.
This suction mechanism stimulates blood flow, lymphatic drainage, and promotes the body’s natural healing response. While hijama cupping can be customized based on individual needs, it generally targets pain relief, detoxification, immune boosting, and relaxation. It’s important to note that hijama cupping is more than just a physical treatment; it embodies a holistic philosophy emphasizing energy balance and well-being.
Origins and Cultural Significance
The roots of hijama cupping trace back centuries, deeply embedded in Islamic tradition as well as ancient Chinese medicine. In Islamic culture, hijama is considered a Sunnah—a recommended practice—as narrated by Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him). Its cultural significance transcends religious boundaries, recognized globally for its therapeutic effects.

Modern Perspective and Acceptance
In contemporary healthcare, hijama cupping is gaining popularity as a complementary therapy. Many practitioners integrate it alongside conventional treatments, emphasizing its safety when performed properly. The increased interest also spurs scientific inquiries into its mechanisms, aiming to understand its physiological impacts better.
How It Works
The core principle of hijama cupping involves creating negative pressure through suction. This causes the skin and underlying tissues to rise into the cup, increasing local blood circulation and stimulating nerve endings. The process helps in releasing toxins, reducing inflammation, and alleviating muscle tension.
Safety and Regulation
While hijama cupping offers numerous potential benefits, it’s crucial that it’s performed by trained professionals under hygienic conditions. Proper sterilization of equipment, correct placement, and knowledge of anatomy are essential to avoid adverse effects. It’s also necessary for individuals with certain health conditions to consult healthcare providers prior to trying hijama.
What is hijama cupping
Understanding what is hijama cupping requires exploring its methodology, intended outcomes, and underlying principles. It’s more than mere physical therapy; it’s a holistic approach rooted in traditional wisdom designed to restore balance within the body.
Definition and Core Principles
What is hijama cupping? At its essence, it is a therapeutic procedure involving the application of cups on specific points of the body—commonly on the back, neck, shoulders, or limbs—to create a vacuum. This vacuum induces suction, which mobilizes blood flow, relaxes muscles, and facilitates the removal of toxins and stagnation.
Unlike some modern therapies that focus solely on symptom relief, hijama aims to address root causes by restoring the free flow of energy, or ‘chi,’ in traditional Chinese medicine, and balancing humors in other traditions. This dual focus on physical and energetic health makes hijama a comprehensive therapy.
Technique and Process
The process typically starts with cleaning the skin area, followed by applying a lubricating substance like oil or lotion to help the cups form a seal. The practitioner then creates suction either manually with a pump or using fire-based methods in traditional techniques. Once the cups are in place, they remain for several minutes, during which patients may experience sensations ranging from tingling to mild discomfort.
In some cases, practitioners perform wet hijama, which involves superficial incisions to facilitate bloodletting, believed to enhance detoxification. More commonly, dry hijama employs suction without incisions. The choice depends on individual health status and practitioner preference.
Physiological Effects
Hijama cupping stimulates blood circulation, helping oxygenate tissues and remove metabolic waste. The suction effect can loosen adhesions, reduce muscle tension, and promote lymphatic drainage. Additionally, it may modulate nervous system activity, leading to pain relief and relaxation.
Emerging scientific studies suggest that hijama could influence neurochemical pathways, immune responses, and even hormonal balances, although further research is needed. Its ability to activate the body’s self-healing mechanisms underscores its potential as a supportive therapy.
Common Uses and Conditions Treated
Practitioners utilize hijama for a wide array of health issues, including chronic pain, migraines, respiratory conditions, musculoskeletal disorders, detoxification, and stress management. Patients seeking holistic wellness often turn to hijama as part of their preventive health strategy.
What is difference between hijama cupping with dry cupping
One of the common questions surrounding hijama cupping relates to how it compares with dry cupping, a simpler form of the same technique. Understanding what is the difference between hijama cupping with dry cupping is essential to make informed decisions and choose the appropriate therapy for your needs.
The Basic Concept of Dry Cupping
Dry cupping is a non-invasive procedure where cups are placed on the skin to produce suction without any bloodletting or incisions. It’s primarily used to relieve muscle tension, improve blood flow, and reduce inflammation. Since it involves no incisions or blood removal, dry cupping is widely regarded as safe and suitable for most individuals.
Key Differences in Technique
In contrast, hijama cupping often involves wet hijama, which includes superficial cuts to facilitate blood removal. This distinction significantly influences the clinical purpose and safety profile of the two modalities.
- Dry cupping relies solely on suction, making it less invasive.
- Hijama cupping, particularly wet hijama, involves both suction and controlled bloodletting, aimed at detoxification and removing ‘stagnant’ blood.
Therapeutic Goals and Outcomes
While both techniques share common ground in promoting blood circulation and relaxation, hijama’s inclusion of bloodletting allows it to target specific health issues related to toxin accumulation and blood impurities. Many practitioners believe that wet hijama offers superior detoxification benefits; however, it also requires meticulous hygiene and skilled execution.
Safety Considerations
What is the difference between hijama cupping with dry cupping in terms of safety? Since wet hijama involves incisions, there is a higher risk of infection if performed improperly. Conversely, dry cupping, being non-invasive, carries minimal risk but might be less effective for certain detoxification purposes.
Preference Based on Condition and Comfort
Individuals seeking pain relief or superficial muscle relaxation might prefer dry cupping due to its simplicity and safety. Those aiming for deeper detoxification, symptom management, or chronic condition treatment may opt for wet hijama under professional supervision.
Summary of Differences
- Invasiveness: Hijama involves bloodletting; dry cupping does not.
- Purpose: Hijama addresses detoxification and blood-related health issues; dry cupping focuses on muscular tension and circulation.
- Safety: Dry cupping is safer for general use; hijama requires expert handling.
- Application: Wet hijama is more complex and requires sterile conditions; dry cupping is straightforward and easy to administer.
Top benefits of hijama cupping for health and wellness
Hijama cupping offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond simple relaxation. From improving physical health to enhancing mental clarity, the therapy’s holistic approach addresses multiple facets of wellbeing.
Pain Relief and Musculoskeletal Health
One of the primary reasons individuals seek hijama is for relief from chronic pain, especially in the back, neck, shoulders, and joints. The suction action increases blood flow to strained muscles, alleviating stiffness and soreness.
Research indicates that hijama can effectively reduce pain by modulating inflammatory markers and promoting tissue regeneration. Patients suffering from migraines, arthritis, or sports injuries have reported significant improvements after regular sessions.
Detoxification and Blood Purification
A key benefit attributed to hijama cupping—particularly wet hijama—is its purported ability to detoxify the body. By removing stagnant blood and toxins, the therapy is believed to enhance overall immunity and prevent disease.
While scientific evidence varies, many practitioners observe improved skin health, clearer complexion, and increased energy levels, suggesting better elimination of impurities. This detoxification process also supports digestive health and metabolic function.
Circulatory Enhancement and Immune Boosting
Cupping stimulates microcirculation, allowing oxygen and nutrients to reach tissues more effectively. This enhanced circulation assists in faster recovery from injuries and strengthens the immune system.
Some studies suggest that hijama may influence cytokine production, which plays a role in immune regulation, thereby contributing to improved resistance against infections. This property makes hijama a supportive therapy during seasonal changes or illness.
Stress Reduction and Mental Clarity
Beyond physical advantages, hijama cupping contributes to mental health by inducing relaxation and reducing stress hormones like cortisol. The soothing sensation and improved sleep quality are side benefits appreciated by many users.
Practitioners also emphasize the energetic balancing aspect, which can lead to emotional stability and mental clarity. Incorporating hijama into holistic wellness routines can thus foster resilience and emotional well-being.
Additional Benefits and Considerations
- Skin health: Improved blood flow can result in healthier skin texture and reduced acne or blemishes.
- Menstrual regulation: Some women find relief from menstrual discomfort.
- Respiratory health: Supportive in managing asthma or bronchitis symptoms.
It’s worth noting that individual results vary, and hijama cupping should complement ongoing medical treatment rather than replace it entirely.
Types of cupping therapy
Cupping therapy is diverse, with different types tailored to specific needs, techniques, and philosophical backgrounds. Understanding types of cupping therapy enables individuals to choose the method best suited for their health goals.
Dry Cupping
As previously discussed, dry cupping involves creating a suction on the skin without incisions. It’s often used for muscle relaxation, improving circulation, and general wellness.
- Application: Suction cups are placed on targeted areas and left for several minutes.
- Benefits: Safe, non-invasive, easy to perform, suitable for beginners.
- Limitations: Less effective for detoxification compared to wet hijama.
hijama cupping
Wet Cupping (Hijama)
Wet hijama combines suction with superficial bloodletting, making it more intensive.
- Method: After creating suction, small superficial incisions are made to allow blood to flow into a collection vessel.
- Applications: Used for detoxification, treating chronic ailments, and removing ‘stagnant’ blood.
- Safety Considerations: Requires sterile environment and qualified practitioners to prevent infections.
Moving or Dynamic Cupping
This variation involves moving cups along the skin surface to massage tissues, often combined with oil.
- Technique: Cups are attached and gently moved to stimulate circulation.
- Uses: Muscular relaxation, lymphatic drainage, and cosmetic purposes such as cellulite reduction.
- Advantages: Combines massage benefits with cupping, providing a dynamic therapeutic experience.
Fire Cupping versus Mechanical Pump Cupping
- Fire Cupping: Traditional method where fire removes oxygen from the cup, creating a vacuum.
- Pump Cupping: Modern technique uses mechanical pumps to generate suction, offering precise control and safety.
Cupping for Specific Conditions
Certain types are tailored for particular health issues:
- Facial cupping: Gentle suction for skin rejuvenation.
- Gua sha and cupping: Often combined for musculoskeletal problems.
- Hospital-grade cupping: Used in clinical settings with strict hygiene standards.
Cupping Equipment Variations
Cups may be made from glass, silicone, bamboo, or plastic, each offering different tactile properties and ease of use. Accessories like adjustable pumps enhance the control over suction intensity.
Choosing the Right Type
Your choice depends on:
- Your health condition
- Personal comfort level
- Practitioner expertise
- Desired outcomes
Consulting a qualified therapist ensures you select the most appropriate cupping method aligned with your wellness goals.
Who can try hijama cupping
Determining who can try hijama cupping involves understanding individual health status, contraindications, and personal circumstances. While hijama offers numerous benefits, it’s not suitable for everyone without proper consultation.
Ideal Candidates for Hijama
Most healthy adults can consider hijama cupping, especially as a preventive or holistic health measure. Its versatility makes it accessible to those seeking pain relief, detoxification, or relaxation.
Key groups include:
- Individuals experiencing muscular pain or tension
- Those looking to boost immunity and overall vitality
- People seeking alternative approaches to manage chronic conditions
- Athletes aiming for faster recovery and injury prevention
- Individuals interested in traditional herbal and energy therapies
Special Population Considerations
Certain groups require caution or medical clearance before trying hijama:
- Pregnant women, especially in the first trimester, due to the risk of inducing contractions
- People with bleeding disorders or on anticoagulant medications
- Patients with anemia or low blood pressure
- Individuals with active infections or skin diseases at the site of treatment
- Patients with heart conditions or uncontrolled hypertension
- Those with recent surgery or open wounds
Consulting Healthcare Providers
Before undergoing hijama, it’s advisable to consult your physician, especially if you have pre-existing health issues. A thorough assessment helps ensure safety and maximizes the potential benefits.
Ethical and Cultural Factors
In some contexts, cultural beliefs influence perceptions of hijama. Respect for personal choices and understanding the therapy’s cultural roots foster a positive experience.
Psychological Readiness
Comfort level and psychological preparedness are important. Some individuals may feel anxious about bloodletting or the invasive nature of wet hijama. Clear communication with the practitioner about concerns enhances trust and comfort.
What important notes when try hijama cupping
Ensuring safety and effectiveness when trying hijama cupping requires awareness of several essential precautions and guidelines. Proper understanding of what important notes when try hijama cupping can significantly impact your overall experience and health outcomes.
Pre-Treatment Precautions
- Health assessment: Have a detailed discussion with your practitioner about your medical history, current medications, and specific health concerns.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water before the session to facilitate detoxification and reduce post-treatment discomfort.
- Avoid heavy meals: Refrain from eating a large meal immediately before hijama to prevent discomfort.
- Skin preparation: Ensure the treatment area is clean and free from lotions or oils unless instructed otherwise.
During the Procedure
- Qualified practitioner: Always choose a licensed, experienced practitioner trained in hijama techniques.
- Sterile equipment: Confirm that all tools and cups are sterilized to prevent infections.
- Communication: Inform the practitioner about any unusual sensations or discomfort experienced during the process.
- Suction control: The suction level should be appropriate, avoiding excessive force that might cause unnecessary pain or bruising.
Post-Treatment Care
- Rest and hydration: Allow the body to recover by resting and drinking fluids.
- Wound care: For wet hijama, keep incisions clean and avoid touching the area unnecessarily.
- Monitoring: Watch for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or pus, and seek medical attention if needed.
- Avoid strenuous activities: Refrain from intense exercise or heavy lifting immediately after hijama.
Safety and Contraindications
- Do not attempt DIY hijama: The procedure must be performed by trained professionals to minimize risks.
- Avoid in certain conditions: If you have bleeding disorders, are pregnant, or have certain chronic illnesses, hijama may be contraindicated.
- Medication considerations: Anticoagulants increase bleeding risk; consult your doctor before proceeding.
- Timing considerations: Avoid hijama during menstruation or when fatigued.
Additional Tips for Success
- Follow practitioner instructions: Adhere to any specific recommendations provided for post-treatment care.
- Maintain hygiene: Keep the treated area clean and avoid exposure to dirt or sweat initially.
- Schedule follow-ups: Regular sessions may enhance benefits, but spacing is crucial to allow proper healing.
Ethical and Cultural Sensitivity
Respect cultural practices and beliefs associated with hijama, and ensure your expectations are realistic and grounded in understanding the therapy’s scope.https://www.google.com/knowledgegraphshares?client=mobilesearchapp&sca_esv=b028dc8ec1d9dff5&bih=879&biw=428&channel=iss&cs=0&hl=vi&rlz=1MDAPLA_viAE995AE995&v=372.0.765951532&sxsrf=AE3TifM54Yon2BzKzAbwaxh-sMX16CRcag:1750078915591&kgmid=/g/11ldd2b847&q=Thai+massage+-+spa+massage+home+service+downtown+Dubai&shndl=30&shem=lcuae,uaasie&source=sh/x/loc/tile/m1/5&kgs
Conclusion
Hijama cupping is a revered traditional therapy with a rich heritage spanning centuries and continents. Its multifaceted benefits—from pain relief and detoxification to immune enhancement and mental clarity—highlight its potential as a valuable addition to holistic wellness routines. Understanding what is hijama cupping, the differences from dry cupping, and the various types helps individuals make informed choices aligned with their health needs. Recognizing who can safely undergo hijama and adhering to critical safety notes ensures a beneficial and secure experience. As research continues to explore its mechanisms and efficacy, hijama cupping remains a compelling blend of ancient wisdom and modern health consciousness, supporting the pursuit of overall health and vitality.https://jobedubaispa.com/massage-2/
